Expense Management
Expense Management in Hbl's simpleBillBook allows you to record, track, and analyze all business expenditures. Proper expense management is essential for financial control, tax compliance, budget monitoring, and understanding your business's operational costs.
Overview of Expense Management
Expense Management helps you:
- Record Business Expenditures: Track all money spent on business operations
- Monitor Spending: Keep a close watch on where your money is going
- Tax Preparation: Maintain accurate records for tax deductions
- Budget Control: Compare actual spending against budgets
- Financial Analysis: Understand expense patterns and trends
Viewing Expenses
To view all expense entries:
- Navigate to Manage Expense → Expense from the main sidebar
- You'll see a comprehensive table listing all expense transactions
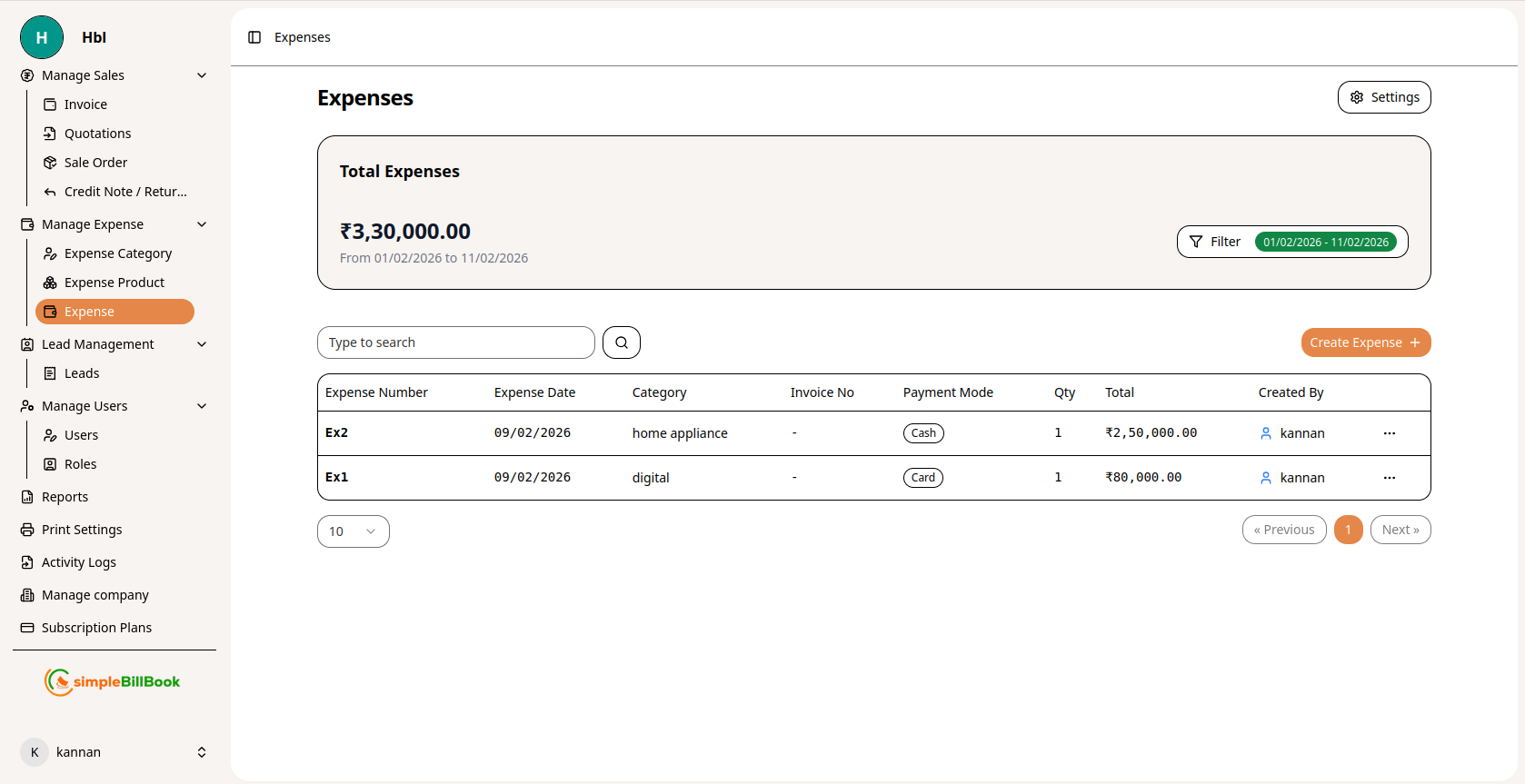 Figure 1: Expenses list showing all expense transactions with details
Figure 1: Expenses list showing all expense transactions with details
Expense Table Columns:
Transaction Identification:
- Expense Number: Unique identifier (e.g., Ex1, Ex2, Ex3)
- Expense Date: Date when expense was incurred
- Category: Expense category (e.g., home appliance, digital)
Financial Details:
- Invoice No: Vendor invoice reference number
- Payment Mode: Method of payment (Cash, Card, Bank Transfer, etc.)
- Qty: Quantity of items purchased
- Total: Total expense amount
- Created By: User who recorded the expense
Key Metrics Displayed:
- Total Expenses: Sum of all expenses in the selected period
- Date Range: Current filter period (e.g., 01/02/2026 to 11/02/2026)
Interface Elements:
- Type to search: Search functionality for finding specific expenses
- Pagination: Items per page control (e.g., "10")
- Filter: Date range and category filtering options
Creating a New Expense Entry
Step 1: Access Expense Creation
From the expenses page, click Create Expense or similar button.
Step 2: Fill Expense Details
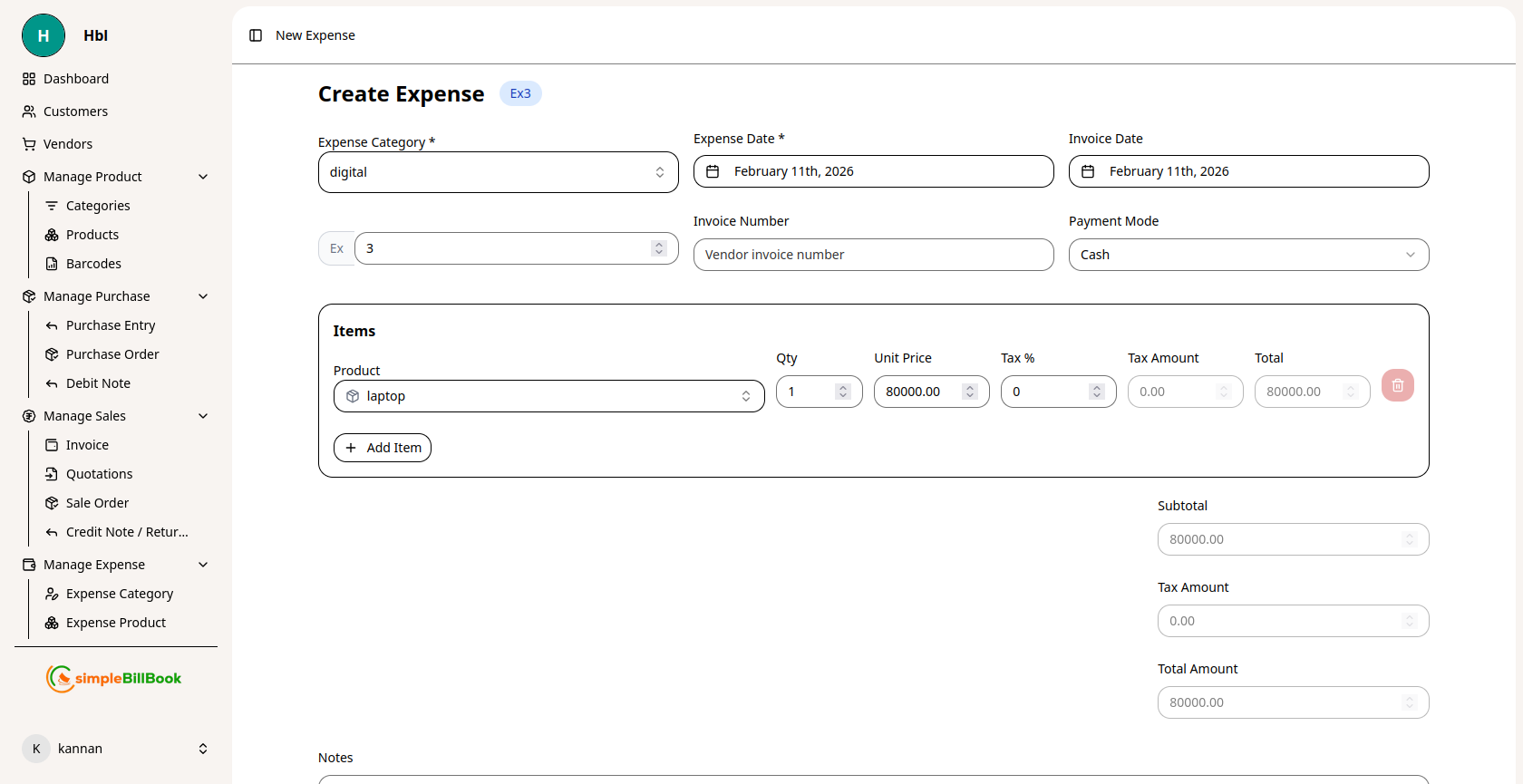 Figure 2: Form for creating new expense entries
Figure 2: Form for creating new expense entries
Header Information:
- Expense Category*: Select from existing expense categories (required)
- Expense Date*: Date when expense occurred (required, defaults to current date)
- Invoice Number: Vendor invoice reference (optional)
- Payment Mode: Select payment method (Cash, Card, Bank Transfer, etc.)
- Expense Number: Auto-generated based on settings (e.g., Ex3)
Item Selection:
- Click Add Item to add expense items
- Select Item from expense products list
- Enter Qty: Quantity purchased
- Unit Price: Cost per unit
- Tax %: Applicable tax rate
- Tax Amount: Auto-calculated tax
- Total: Line item total (auto-calculated)
Financial Summary:
- Subtotal: Sum of all item totals before tax
- Taxes: Total tax amount
- Total Amount: Final expense amount including taxes
Additional Information:
- Notes: Additional details or comments about the expense
Step 3: Save Expense Entry
- Click Save to record the expense
- Click Cancel to discard the entry
Expense Settings Configuration
Accessing Expense Settings
From the expenses page, access settings via gear icon or Settings button.
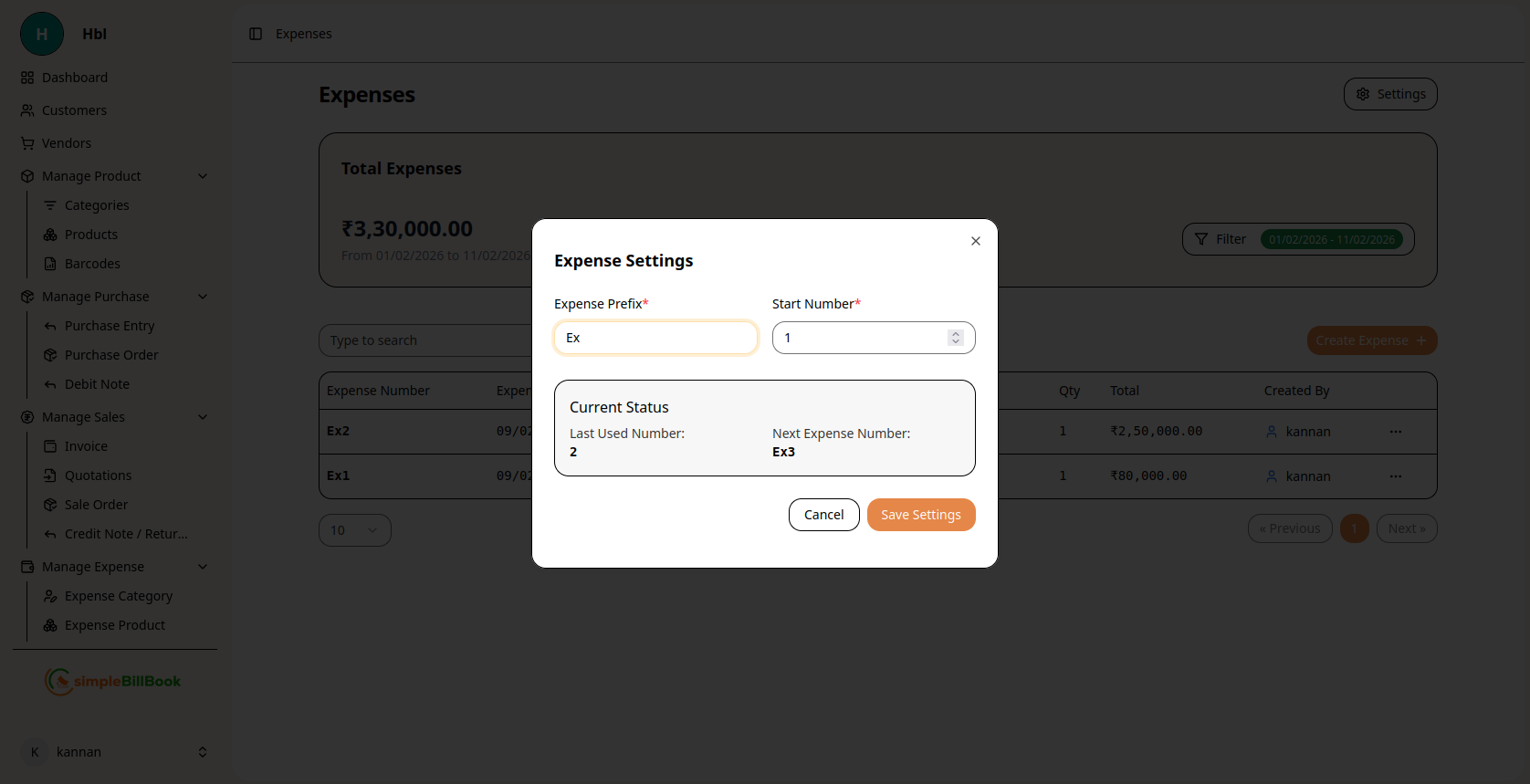 Figure 3: Configuration settings for expense numbering
Figure 3: Configuration settings for expense numbering
Configurable Settings:
Numbering System:
- Expense Prefix: Custom prefix for expense numbers (default: "Ex")
- Start Number*: Beginning sequence number (required)
- Current Status: System tracks last used number
- Next Expense Number: Preview of next auto-generated number
Other Settings:
- Default Payment Mode: Preferred payment method for new expenses
- Default Category: Default expense category for quick entry
- Tax Configuration: Default tax rates for expense items
Saving Settings:
- Click Save Settings to apply changes
- Use Cancel to discard modifications
- Settings affect all future expense entries
Expense Workflow
Complete Expense Recording Process:
1. Preparation Stage:
- Verify expense category exists or create new one
- Ensure expense product exists or create new one
- Gather supporting documentation (receipts, invoices)
2. Expense Entry:
- Select appropriate category
- Enter expense items and quantities
- Record payment method and details
- Add invoice reference number
3. Documentation:
- Attach receipts or invoices if supported
- Add notes for audit trail
- Record for tax purposes
4. Review and Approval:
- Verify accuracy of amounts
- Approve if approval workflow is enabled
- Flag any discrepancies
5. Reporting and Analysis:
- Expense appears in financial reports
- Updates category spending totals
- Affects profit and loss calculations
Types of Payment Modes
Common Payment Methods:
- Cash: Physical currency transactions
- Card: Credit card or debit card payments
- Bank Transfer: Online fund transfers, NEFT, RTGS
- Cheque: Paper cheque payments
- UPI: Digital payment apps
- Credit: Supplier credit (pay later)
- Wallet: Digital wallets
Best Practices for Expense Management
1. Timely Recording
- Record expenses as soon as they occur
- Don't wait until month-end
- Reduces risk of forgotten transactions
2. Supporting Documentation
- Always keep receipts and invoices
- Attach digital copies when possible
- Maintain organized filing system
3. Accurate Categorization
- Use consistent expense categories
- Train staff on proper categorization
- Review categories periodically
4. Regular Reconciliation
- Reconcile expenses with bank statements
- Verify totals match actual payments
- Investigate discrepancies promptly
5. Approval Workflow
- Implement approval for large expenses
- Define spending limits by role
- Maintain audit trail of approvals
Integration with Other Modules
Expense Category Management:
- Category Selection: Expenses link to expense categories
- Category Analysis: Track spending by category
- Budget Monitoring: Compare actual vs. budget by category
Expense Product Management:
- Product Selection: Pre-defined expense products for quick entry
- Pricing History: Track purchase price changes over time
- Consistent Coding: Standardized HSN codes and tax rates
Vendor Management:
- Expense by Vendor: Track spending with specific vendors
- Payment History: Monitor payment patterns
- Vendor Performance: Evaluate vendor pricing and reliability
Financial Reporting:
- Profit & Loss: Expenses reduce business profit
- Cash Flow: Outgoing payments affect cash position
- Tax Reports: Track deductible expenses for tax filing
Common Scenarios and Solutions
Scenario 1: Recurring Monthly Expenses
Solution:
- Create expense products for recurring items
- Use same categories each month
- Set reminders for regular expenses
Scenario 2: Split Expenses Across Categories
Solution:
- Create multiple line items in single expense entry
- Assign different categories to each item
- Maintain single transaction reference
Scenario 3: Expense Without Invoice
Solution:
- Record expense with available details
- Note "No Invoice" in invoice number field
- Attach alternative documentation if available
Scenario 4: Reimbursable Employee Expenses
Solution:
- Record expense under employee name
- Mark as reimbursable if applicable
- Track reimbursement status separately
Scenario 5: Advance Payments
Solution:
- Record as prepaid expense
- Adjust when actual expense occurs
- Track advance balance separately
Reports and Analytics
Available Expense Reports:
- Expense Summary: Total expenses by category and period
- Category Analysis: Detailed breakdown by expense category
- Payment Mode Analysis: Expenses by payment method
- Vendor Expense Report: Spending grouped by vendor
- Monthly Trend: Expense patterns over time
- Budget vs. Actual: Compare actual spending against budgets
Key Metrics to Monitor:
- Total Expenses: Overall business spending
- Expense by Category: Which categories have highest spending
- Expense Growth: Month-over-month spending changes
- Payment Mode Preference: Most used payment methods
- Average Expense Value: Typical transaction size